As the largest size interface on the motherboard, the PCI-E interface has a wide range of applications, so it is different from other PCI and AGP. Today, Xiaobian will share it.
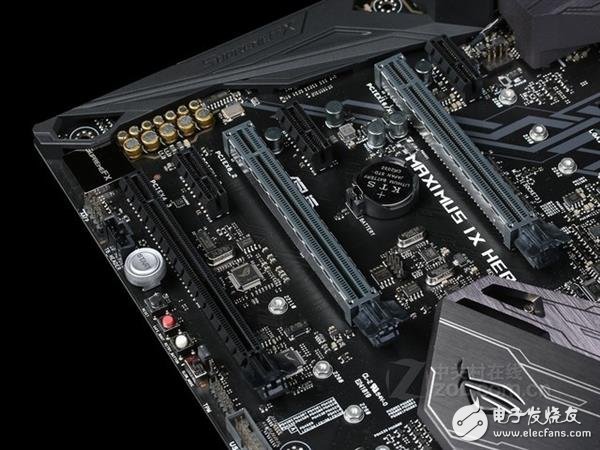

The PCI-E interface is a relatively common interface standard on the motherboard. It is mainly used for devices that need to communicate directly with the CPU. It is usually used to expand the functions that are not supported on the motherboard, such as expanding the discrete graphics card. The purpose is to The platform outputs more powerful graphics capabilities to make up for the lack of nuclear display.

Recently, you may have heard more about the solid state drive of the PCI-E interface or the solid state drive of the M.2 interface. As long as the SSD products supporting the NVMe protocol are through the PCI-E bus. Processor interaction, up to the current support for PCI-E 3.0 X4 bandwidth, the issue of this bandwidth, I will explain later.
PCI interface
PCI bus English is called Peripheral Component Interconnect, translated into Chinese is "peripheral device interconnection", is a partial parallel bus standard introduced by PCISIG (PCI Special Interest Group). The PCI bus standard was developed in 1992, and the calculation is larger than the age of the wolf. His appearance was developed by the ISA (Industy Standard Architecture) bus.
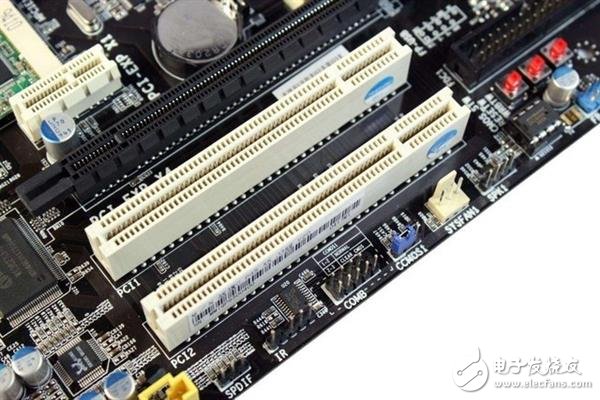
PCI interface
The normal PCI interface data width is 32 bits (bit, also known as small b), the interaction speed is 33MHz, the theoretical maximum bandwidth is 4Byte/s*33MHz=133MB/s, note that it becomes Byte byte. That is to say, the big B is usually said. Since the data is calculated in binary in the computer, the 33MHz in this equation should actually be 33.33333. . . .
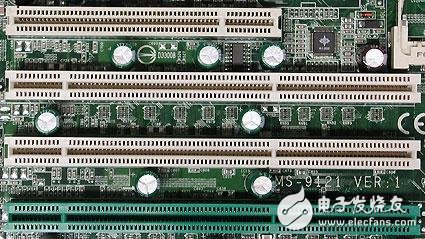
PCI (top) and PCI-X (bottom)
Later, the PCI-X with higher transfer speed is still the PCI bus standard, which increases the speed by increasing the number of pins. In addition, the new PCI 64/66 specification provides a 64-bit data width and a 66 MHz operating frequency. The theoretical bandwidth has increased to 533MB/s. This idea seems to be the combination of two PCI interfaces, but not exactly the same.
AGP interfaceAGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is a new standard developed on the basis of PCI bus, which is specially designed for higher and higher image processing requirements. However, its main purpose is to solve the problem between display card and processor. Communication problem, so it is only a "port", "this means that it can only connect to a terminal and this terminal must be a graphics accelerator card. PCI is a bus, it can connect many different kinds of terminals, can be Graphics card, can also be a network card or SCSI card, as well as a sound card, and so on." (quoted from Baidu Encyclopedia, AGP slot entry)

AGP interface
AGP follows the PCI specification, 32-bit data width, but the operating frequency starts at 66MHz, and the AGP1X specification can provide 266MB/s theoretical bandwidth. In the AGP2X version, a new bidirectional data transfer technique (one data for each of the rising and falling edges) was used, and the theoretical bandwidth doubled to 533MB/s.
After the geometric processing of the screen processing demand, the bandwidth of AGP2X is not enough. AGP4X came into being, and the working frequency has not changed. By increasing the data width, the theoretical bandwidth has been doubled to 1066MB/s. Later, the AGP8X version was introduced to double the bandwidth again to 2133MB/s.
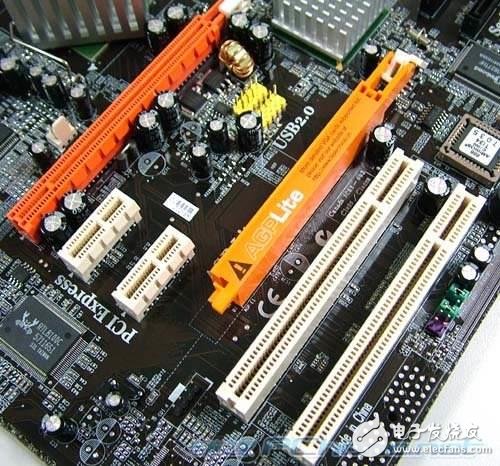

AGP interface that coexists with the PCI-E interface (picture from the network)
In the latter stage, when AGP's high occupancy defects were highlighted and bandwidth improvement became difficult, in 2002, PCI Express was also confirmed as PCI-E standard. However, due to the high price at the beginning, there was a motherboard with AGP and In the case of the PCI-E interface, for a long time, the user still insisted on selecting an AGP graphics card to install the machine.
PCI-E interfaceFinally, it has reached the top priority, PCI-E interface, which is also the most widely used universal interface. The bandwidth is divided into 1X/2X/4X/8X/16X. At present, other interfaces are rarely seen on the motherboard, mainly PCI-E. Expansion interface, 2X slot is also relatively rare.
The PCI-E interface changes the parallel data transmission mode used by PCI and AGP to the serial transmission mode. The advantage of serial transmission is that the transmission speed can be faster. The disadvantage is that data loss is easy, but this defect is in the face of new technologies that are constantly improving. It is no longer a problem.

The PCI-E 1.0 standard provides 2.5 GT/s (Giga Transmission per second, which is the number of transmissions per second, different from Gbps). The commonly used PCI-E X16 provides 16-bit data. Width, its unidirectional theoretical bandwidth can already reach 5GB / s. Because it is a serial transmission, PCI-E 2.0 used to adopt the 8-bit/10bit standard. When transmitting data, it will increase the "start flag and termination flag". The actual transmission of 8 bits of data requires 10 bits of transmission, so the actual The one-way transmission speed is approximately 4 GB/s. Even this is far more than the 2.1GB/s of the AGP8X. If you count bidirectional data transfers (one data for each of the rising and falling edges), the actual bandwidth can reach 8GB/s.
The PCI-E 2.0 standard did not make major changes to it, but doubled the 2.5GT/s transfer speed to 5.0GT/s. In the original case, the PCI-E 2.0 X16 has a bidirectional bandwidth of 16GB/s. .
At present, the most widely used PCI-E 3.0 standard upgrades the transmission standard to 8 GT/s and upgrades the transmission standard to 128 bit/130 bit. The coding loss is almost negligible. The theoretical bidirectional bandwidth of PCI-E 3.0 X16 can reach 32 GB/ s.
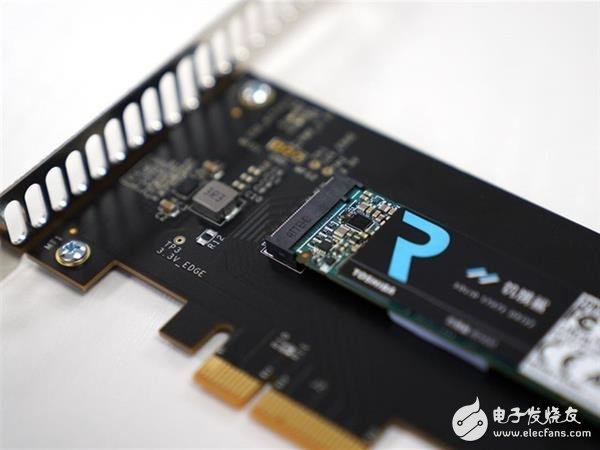

NVMe standard SSD
Recently, the relatively common NVMe protocol SSD uses a PCI-E 3.0 X4 interface that can support up to 8GB/s, but the hard disk cannot be read and written at the same time. The maximum bandwidth can only be one-way 4GB/ s, that is, 32Gb/s, unit conversion 1Byte (bytes) = 8bit (bits).
Solar Energy Mounting Ground Screw Pile
Solar Energy Mounting Ground Screw Pile with N series and F series mainly .N Series Ground Screw with 3pcs,4pcs or 6pcs nut and reinforced plate to assemble ,F Series Ground Screw with flange to assemble solar brackets .
There are two kinds of N series Ground Screw mainly ,with 1 or 2 or 3pcs big blade ,and with Nuts and reinforced plates,another kind of ground screw with continuous small blades .F series ground screw with round,hexagon ,triangle or square flanges .with big blade or continuous blade .
Ground Screw Pile for solar energy mounting system with many advantage : no-digging,no waste time ,lower cost,protect environment,easy install .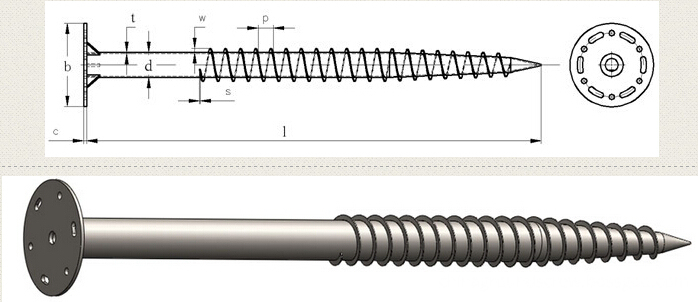
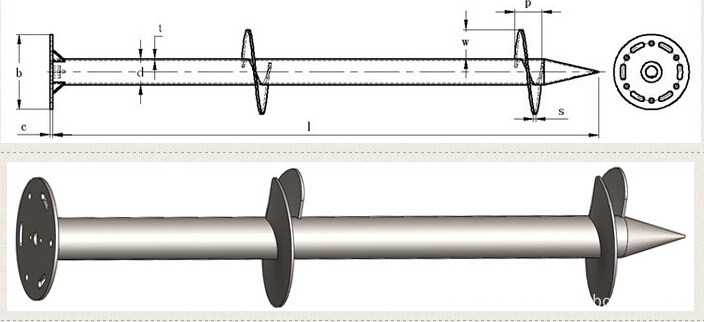
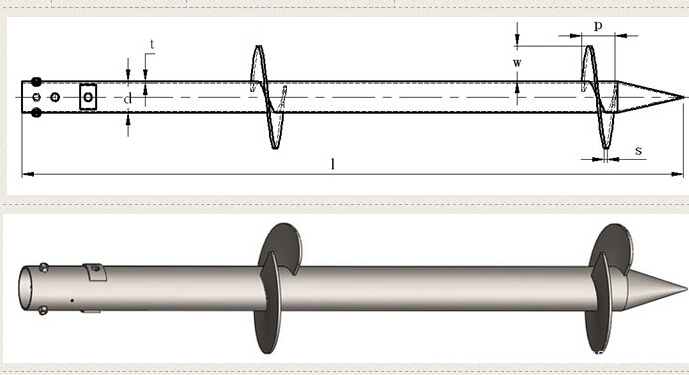
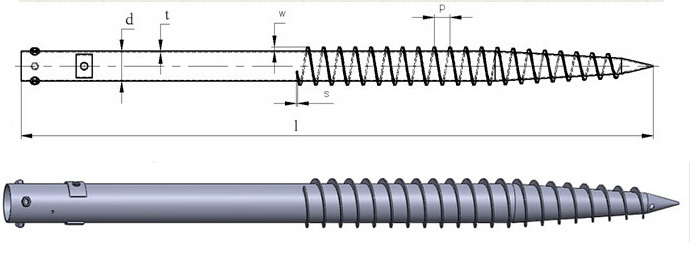
Solar Energy Mounting Ground Screw System,Ground Screw Pile Foundation for Solar,10Kw PV Panel Mounting System,Ground Screw Solar Rack System
BAODING JIMAOTONG IMPORT AND EXPORT CO., LTD , https://www.chinagroundscrew.com