TCP/IP is not a protocol, but a collective term for a family of protocols. It includes IP protocol, IMCP protocol, and TCP protocol.
Here are a few knowledge points that need to be paid attention to:
Internet address: IP address, generally network number + subnet number + host number
Domain name system: In layman's terms, it is a database that can convert a host name into an IP address
RFC: TCP/IP protocol standard document
Port number: a logical number, the mark carried by the IP packet
Socket: Application programming interface
Working characteristics of the data link layer:
Send and receive IP datagrams for IP modules
Send ARP requests and receive ARP responses for the ARP module (ARP: Address Resolution Protocol, which converts IP addresses into MAC addresses)
Send RARP request and receive RARP reply for RARP
Next, let’s take a look at the TCP/IP workflow:
The data link layer obtains data transfer information from ARP, and then obtains specific data information from IP
IP protocol
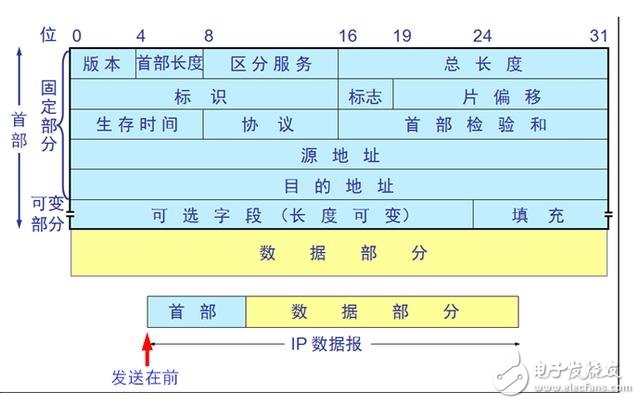
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
Among the IP protocol headers, the most important is the TTL (the maximum number of network segments allowed by IP) field (eight bits), which stipulates that the data packet can pass through several routes before being discarded.
IP routing
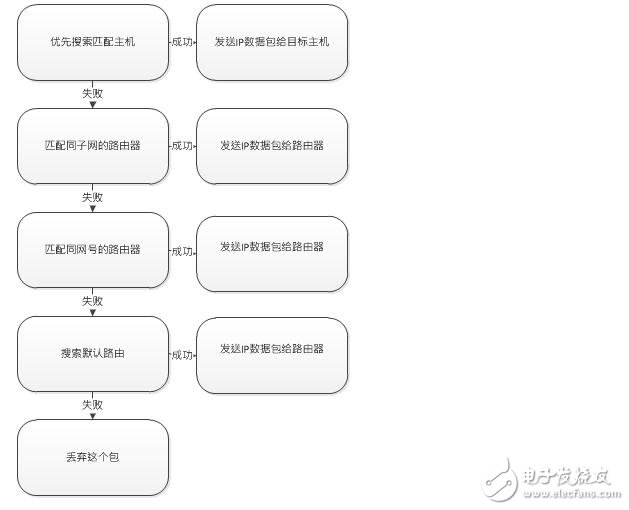
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
The working principle of ARP protocol
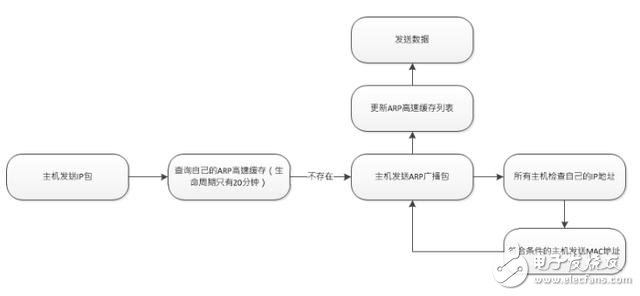
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
ICMP protocol (Network Control Document Protocol)
Send the error message that the IP packet cannot be sent to the host
Query message
Ping query: whether the host is reachable, by calculating the interval time and the number of packets transmitted
Subnet mask
Timestamp: get the current time
Error message
Situations that do not occur:
ICMP error messages do not generate error messages
The source address is zero address, ring destination address, broadcast address, multicast address
IP router selection protocol
Static routing
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
Static routing
Configure the interface to generate routing table entries by default, or use route add to manually add entries
ICMP messages (ICMP redirect messages) update table entries
Dynamic route selection (only used between routes)
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Distributed routing protocol based on distance vector (distance record from router to each destination network)
Work undertaken by router:
Send a RIP request message to each known router, requesting a complete routing table
If you accept the request, hand over your own routing table to the requester; if not, process the IP request table entry (self part + hop count/non-existent part + 16)
Accept the response and update the routing table
Update the routing table regularly (usually 30s, can only be said to be too frequent~)
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First Protocol)
Distributed link state (network with interfaces to these two routers) protocol
When the link status changes, a reliable flooding method is used to send information to all routers (the link status of all adjacent routers)
Finally, a topology diagram of the entire network will be established
TCP/IP three-way handshake, four-time breakup
First, let’s first understand the TCP segment
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
I have also marked the important signs in the picture, and focus on understanding the signs.
ACK: Confirm that the serial number is valid
RST: Reset connection
SYN: initiated a new connection
FIN: release a connection
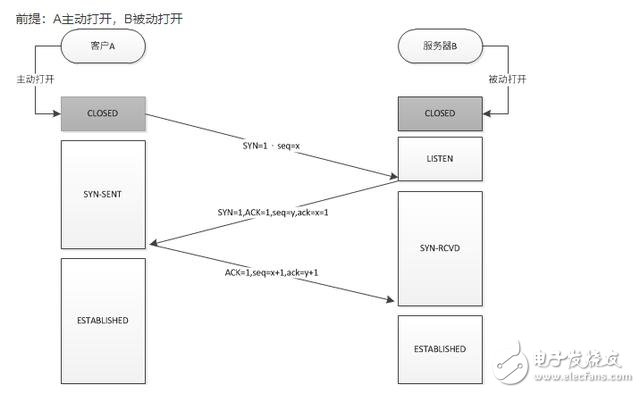
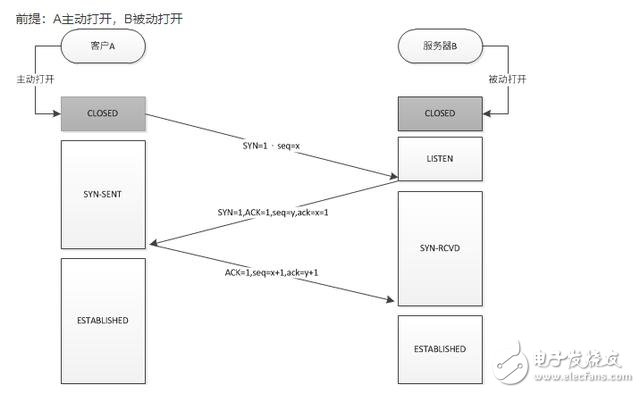
The three-way handshake process (the client is represented by A, and the server is represented by B)
Prerequisite: A is actively turned on, and B is passively turned on
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
Before establishing a connection, B first creates a TCB (Transmission Control Block), ready to accept the connection request of the client process, and is in the LISTEN (listening) state
A first creates a TCB, then sends a connection request to B, sets SYN to 1, and selects the initial sequence number seq=x to enter the SYN-SEND (synchronized sent) state
After receiving the connection request, B sends an acknowledgment to A, SYN is set to 1, ACK is set to 1, and an acknowledgment sequence number ack=x+1 is generated at the same time. At the same time, the initial sequence number seq=y is randomly selected to enter the SYN-RCVD (synchronously received) state
After A receives the confirmation connection request, ACK is set to 1, the confirmation number ack=y+1, seq=x+1, and it enters the ESTABLISHED (connection established) state. A confirmation connection is sent to B, and finally B also enters the ESTABLISHED (connection established) state.
In short, it is
When establishing a connection, the client sends a SYN packet (SYN=i) to the server, and enters the SYN-SEND state, waiting for the server to confirm
When the server receives the SYN packet, it must confirm the client's SYN (ack=i+1), and at the same time send a SYN packet (SYN=k), that is, the SYN+ACK packet, and the server enters the SYN-RECV state.
The client receives the SYN+ACK packet from the server and sends an acknowledgment ACK (ack=k+1) to the server. After the packet is sent, the client and server enter the ESTABLISHED state and complete the three-way handshake.
One point of knowledge interspersed here is a SYN attack, so what is a SYN attack? What are the conditions that happened? How to avoid it?
In the three-way handshake process, after the Server sends the SYN-ACK, the TCP connection before receiving the Client's ACK is called half-open connect. At this time, the Server is in the SYN_RCVD state. When the ACK is received, the Server transfers to ESTABLISHED status. The SYN attack is that the client forges a large number of non-existent IP addresses in a short period of time, and continuously sends SYN packets to the server, the server replies to the confirmation packet, and waits for the client's confirmation. Since the source address does not exist, the server needs to continue to re- Until the timeout expires, these forged SYN packets will occupy the unconnected queue for time, causing normal SYN requests to be discarded because the queue is full, causing network congestion and even system paralysis. SYN attack is a typical DDOS attack. The way to detect SYN attack is very simple, that is, when there are a large number of semi-connected states on the Server and the source IP address is random, it can be concluded that it has been attacked by SYN. ​​Use the following command to make it in force:
#netstat -nap | grep SYN_RECV
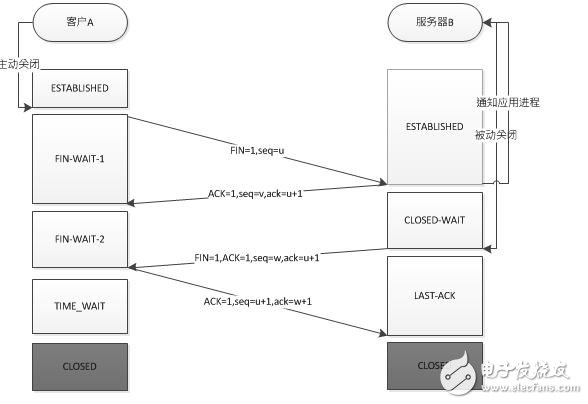
The process of breaking up four times (the client is represented by A, and the server is represented by B)
Since the TCP connection is full-duplex, each direction must be closed separately. This principle is that when one party completes the data sending task, it sends a FIN to terminate the link in this direction. Receipt of a FIN only means that there is no data flow in this direction, and no data will be received, but data can still be sent on this TCP connection. Knowing that FIN is also sent in this direction, the party that first shuts down will take the initiative. Close, and the other party performs passive shutdown.
Prerequisite: A is actively closed, B is passively closed
Summary of TCP/IP protocol detailed explanation (a mouthful of old blood)
For more C/C++ learning materials, please privately write my "code" to get
Someone may ask, why is there a three-way handshake when connecting, but four waves of hands when disconnecting?
This is because the server in the LISTEN state, after receiving the SYN message for establishing a connection request, puts the ACK and SYN in one message and sends it to the client. When the connection is closed, when receiving a FIN message from the other party, it only means that the other party no longer sends data but can still receive data. You may not send all the data to the other party, so you can close immediately or send some After the data is sent to the other party, send a FIN message to the other party to indicate that they agree to close the connection now. Therefore, one's own ACK and FIN are generally sent separately.
A sends a FIN to close the data transfer from A to B, and A enters the FIN_WAIT_1 state.
After B receives the FIN, it sends an ACK to A, confirming that the sequence number is the received sequence number +1 (same as SYN, one FIN occupies one sequence number), and B enters the CLOSE_WAIT state.
B sends a FIN to close the data transmission from B to A, and B enters the LAST_ACK state.
After A receives the FIN, A enters the TIME_WAIT state, and then sends an ACK to B, confirming that the serial number is the received serial number + 1, B enters the CLOSED state, and completes four waves.
Simply put
Client A sends a FIN to close the data transmission from client A to server B (message segment 4).
Server B receives this FIN, it sends back an ACK, confirming that the sequence number is the received sequence number plus 1 (message segment 5). Like SYN, a FIN will occupy a serial number.
Server B closes the connection with client A and sends a FIN to client A (message segment 6).
Client A sends back an ACK message confirmation, and sets the confirmation sequence number to the received sequence number plus 1 (message segment 7).
After A enters the TIME-WAIT state, it will not release TCP immediately. It must wait for the time set by the timer 2MSL (the longest message segment life) before A enters the CLOSED state. why?
In order to ensure that the last ACK segment sent by A can reach B
Prevent "failed connection request segment" from appearing in this connection
OK~ Is it hard to understand? Let’s call it “humaneâ€
Three-way handshake process
The client sends a request "open the door, I want to come in" to the server
The server sends "Come in, I'll open the door for you" to the client
The client has kindly sent a "thank you, I'm coming in" to the server
Four waved process
The client sends "It's late, I'm leaving" to the server, and waits for the server to get up to send him
The server hears it, and sends "I know, then I'll send you out" to the client, and wait for the client to leave
After the server closes the door, it sends a message "I closed the door" to the client, and then waits for the client to leave (Nima ~ hypocritical)
The client sends "I know, I'm leaving", and then he left
Rugged Barcode Scanner,Rugged Barcode,Rugged Scanner,Rugged Handheld Scanner
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com