The cheapest sports bracelet is less than $100, and there are plenty of sports watches, sleep monitors, brain exercises based on EEG technology, relaxation equipment and even devices that monitor blood sugar.
However, despite the emergence of new products, wearable devices have the regret of “wearing short†and “wearing not longâ€. According to Tencent ISUX's "2014 Smart Wearables Market White Paper", 25% of netizens have potential demand for smart wearable devices, but smart wearables have a turnover rate of 87% in three months.
At present, smart wearable devices are moving from sports health to health care, including blood glucose meters, blood pressure meters, etc., causing widespread concern in the capital market. It has to carry not only functions such as pedometer, blood pressure measurement, blood glucose measurement, but also many areas waiting for technological breakthroughs and explorations, such as Alzheimer's disease.
The US technology blog ReadWrite counts the five areas that have the greatest impact on wearable devices in the next few years, including the health care sector.
Data-based medical care
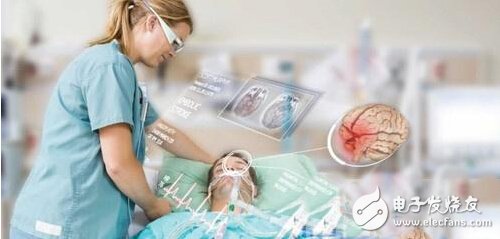
Definition: Continuously collect and display user health and motion information, embedded biosensors and software. This will help doctors, medical teams and coaches make accurate decisions quickly.
Dr. David Berkoff, a sports medicine expert at the University of North Carolina, said: "One of the most important goals at present is to improve the sustainability of medical care. At present, we can only obtain information on the short-term, discontinuous health of patients. When patients see the disease, we understand their situation on the day and make decisions accordingly."
With continuous monitoring, wearable computing devices can fill critical gaps. "With these devices, we will be able to obtain consistent and accurate data on the patient's physical condition and daily behavior. This will help doctors make better decisions and help drive habit changes and outcomes," said Berkov.
Many people believe that the medical field will bring huge space for wearable devices. Although wearables are only one line away from medical devices, this distance is huge. Due to the accuracy and availability of data, it is difficult to obtain the qualification of medical certification for wearable devices. Moreover, the platform for medical wearable devices based on big data is also more formal than content. The challenges faced by wearable devices in the medical field will be extremely cruel.
2. Personalized wearable devices
Definition: Perfect for the user's body, clothing with sensors and medical equipment. Such garments and equipment are manufactured using 3D printing technology to achieve customization.

There are reports that Nike is using nanotechnology to embed sensors into clothing. In the near future, users will be able to use 3D printing technology to make their own smart T-shirts. Athletes and coaches will be better able to understand whether they are overtrained and whether the athlete's body is short of water or too nervous. This will also reduce the cost of production and supply chain management for companies such as Nike.
3D printing with embedded sensors will also change the medical device industry. The Mayo Clinic has developed the first such device. The hospital is exploring how to implant sensors into the device to enhance the monitoring of the patient's physical condition.
3. Health coach service
Definition: Ability to monitor user motion, hardware and clothing embedded in the sensor. Such a device can present the user's motion information and suggest how the user can improve. The next step in the development of wearable technology will help users stay in shape and correct their sitting and walking postures.
If you want such a coaching service to succeed, the key is to ensure the accuracy of the data and optimize the way the data is presented. Dr. Steven LeBoeuf, founder and president of Valencell, is also very concerned about this issue. He said: "One of the reasons we started from the optical signal sensor in the ear is the accuracy of the data."
Leboff said that the next step in the future is to optimize the relevance of the data and increase user engagement. “We need good data and software to deliver accurate data and provide useful advice on how to make progress and how to improve health.â€
4. Gesture-based interface
Definition: A human-machine interface that allows a user to interact with a device through gestures or other body movements. By introducing common actions and gestures into complex machine-based tasks, we can optimize the user experience and make it easier for users to use new devices and software.
With Google Glass, we've seen the start of a gesture-based interface. With Google Glass, users can take photos with just a blink of an eye. Recent Apple patents show that Watch may support gesture-based adaptive learning. This enables a series of operations, such as navigation of a TV set-top box, page turning of the iPad while on a treadmill, and turning off the lights, and the like.
5. Authentication
Definition: A wearable device can be a unique identity for a user. Unique identification data, such as heart rate rhythm, can replace traditional passwords.
You may often forget your password, and your account may have been hacked. These issues may soon be a thing of the past. New technologies, such as watch-type heart rate monitoring devices, measure the user's unique heart rate rhythm and convert it to a password. There are also some devices that automatically log in when the user is close. For example, an Android smart watch and a smartphone can be unlocked when they are close.
Idc Connectors,Idc Socket Connector,Idc Electronic Socket Connector,2.00Mm Socket Connector
Dongguan Yangyue Metal Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.yyconnector.com